Standards Covered
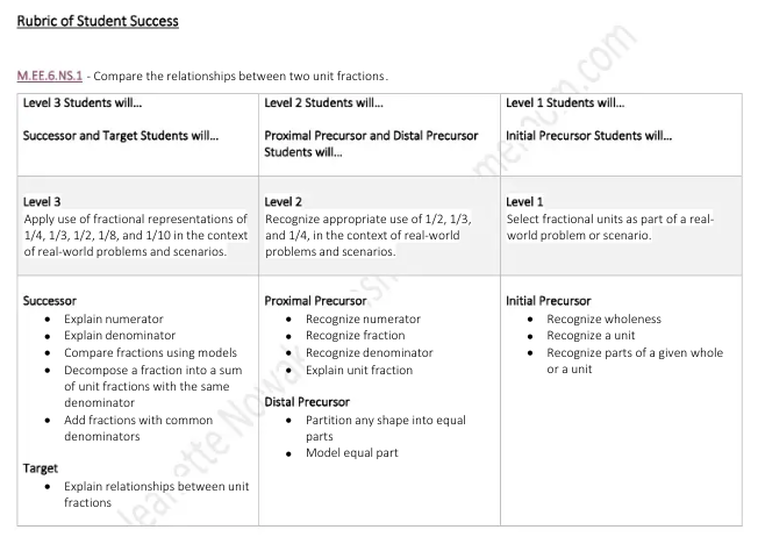
- M.EE.6.NS.1 - Compare the relationships between two unit fractions.
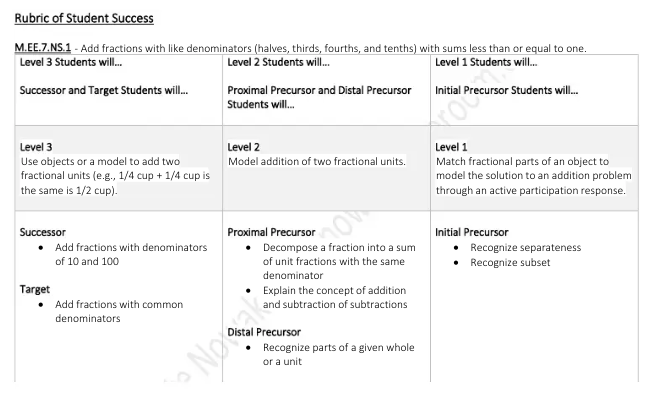
- EE.7.NS.1. Add fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) with sums less than or equal to one.
- EE.8.NS.1. Subtract fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) with minuends less than or equal to one.
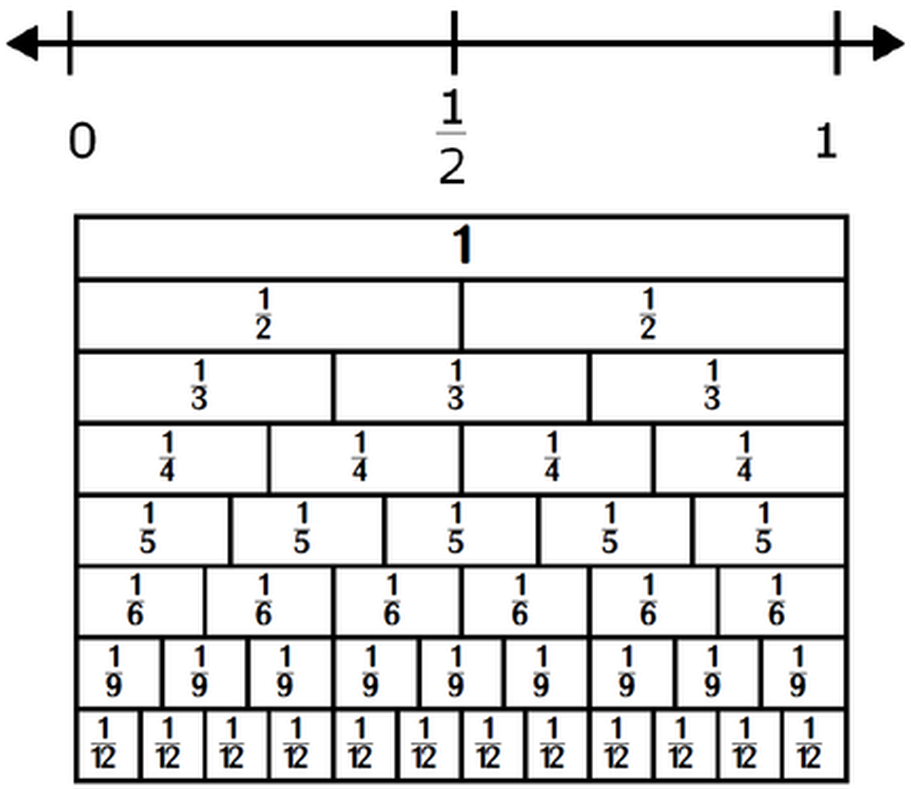
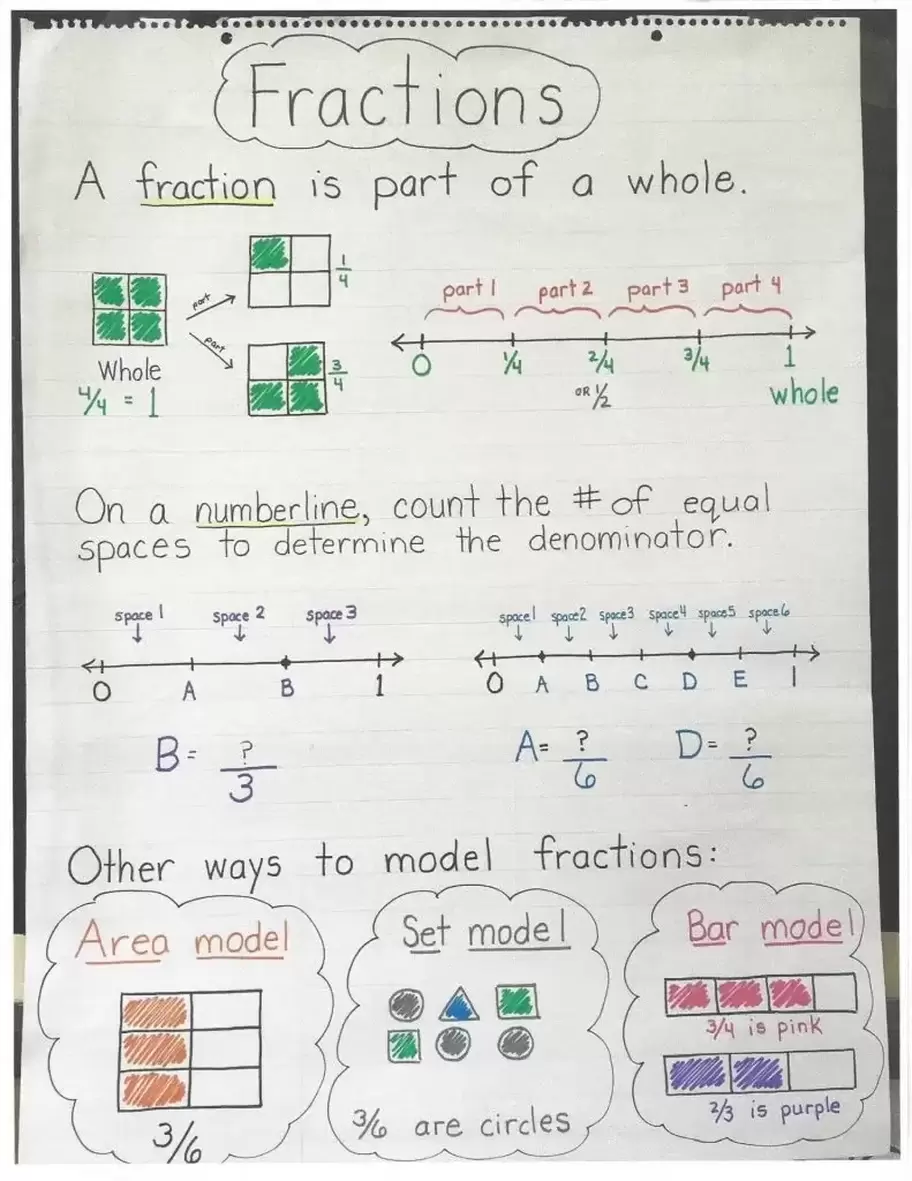
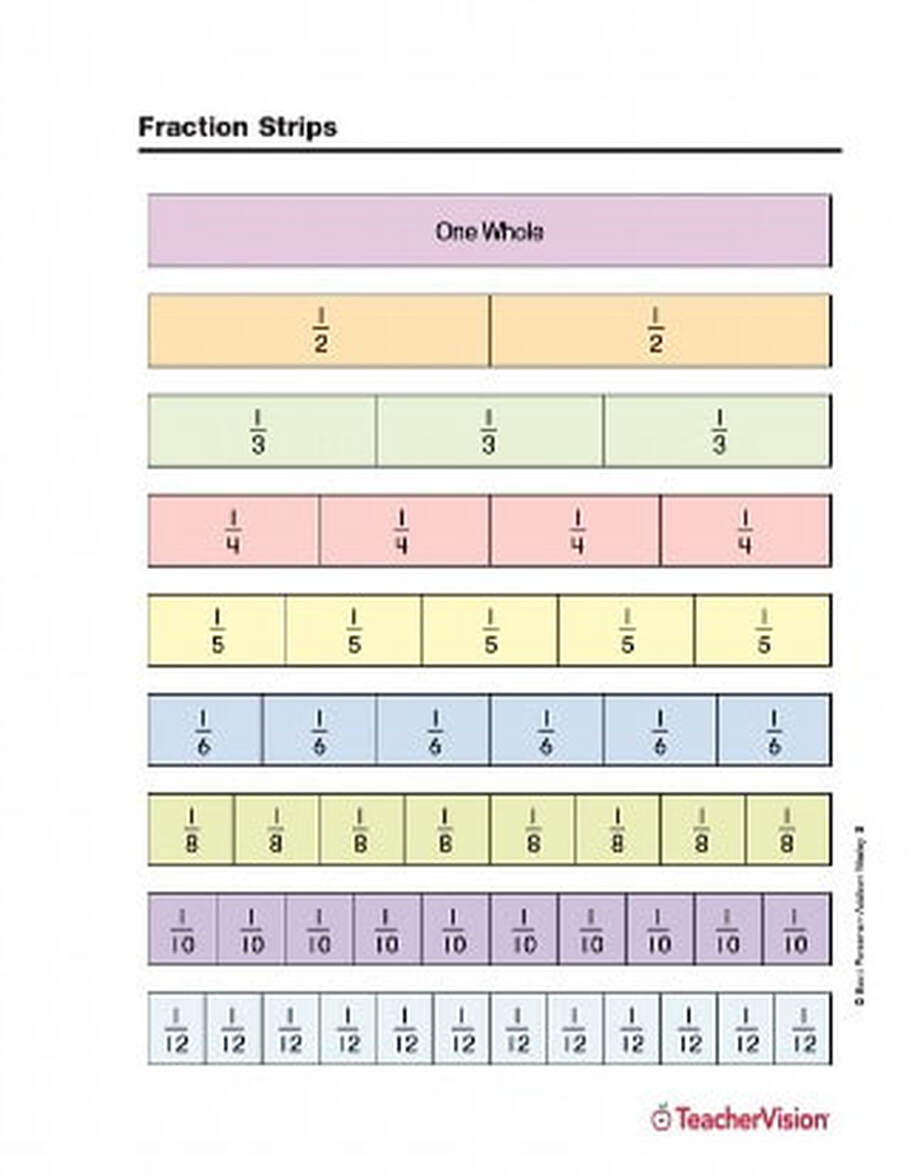
A fraction is a number that represents part of a whole or part of a group. Students need many opportunities to use concrete models to develop familiarity and understanding of fractions. Students need to relate dividing a shape into equal parts and represent this relationship on a number line, where the equal parts are between two whole numbers.
With modeling of real shapes and objects, students should experience opportunities to:
Fractions are ratios that show part-to-whole. The fraction ¼ means that one part is selected from a whole of 4 parts. Understanding fractions builds into skills for ratios and percents.
With modeling of real shapes and objects, students should experience opportunities to:
- Recognize and match equivalent fractional parts.
- Compare fractional parts to determine which is greater, less than or equal.
- Add and subtract fractional parts to make a new fraction.
Fractions are ratios that show part-to-whole. The fraction ¼ means that one part is selected from a whole of 4 parts. Understanding fractions builds into skills for ratios and percents.
M.EE.6.NS.1 - Compare the relationships between two unit fractions.
Learning Goal:
• Level 2-3 – I will compare two unit fractions.
• Level 1 – I will count fractional objects.
Essential Questions:
• How can I represent these fractions?
• What is the relationship between the two fractions?
• Are they equivalent?
• Which fraction is larger/smaller?
Vocabulary:
• numerator - the top number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts of the whole taken.
• denominator - the bottom number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts the whole has been divided into.
• equal - alike in size, value or amount to something else.
• fraction - a representation of a division of a number; a part of a whole.
• half - either of two equal parts of something.
• quarter - one of four equal parts into which something is divided.
• whole number - a positive integer or zero. 1, 15, 30 and 894 are examples.
Learning Goal:
• Level 2-3 – I will compare two unit fractions.
• Level 1 – I will count fractional objects.
Essential Questions:
• How can I represent these fractions?
• What is the relationship between the two fractions?
• Are they equivalent?
• Which fraction is larger/smaller?
Vocabulary:
• numerator - the top number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts of the whole taken.
• denominator - the bottom number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts the whole has been divided into.
• equal - alike in size, value or amount to something else.
• fraction - a representation of a division of a number; a part of a whole.
• half - either of two equal parts of something.
• quarter - one of four equal parts into which something is divided.
• whole number - a positive integer or zero. 1, 15, 30 and 894 are examples.
Learning Intention: Students will identify that a unit fraction is one part of a whole; indicate that the more parts a whole is divided into, the smaller the parts will be.
Success Criteria: Students will be successful when they can independently explain numerator, explain denominator, compare fractions using models, and decompose a fraction into a sum of unit fractions with the same denominator.
Success Criteria: Students will be successful when they can independently explain numerator, explain denominator, compare fractions using models, and decompose a fraction into a sum of unit fractions with the same denominator.
Fractions are important because they tell you what portion of a whole you need, have, or want.
Fractions are used in baking to tell how much of an ingredient to use.
Fractions are used in telling time; each minute is a fraction of the hour.
Money is another place fractions are used. For example, a quarter is one fourth of a dollar (1/4). A dime is one-tenth, represented by 1/10. We could continue by talking about pennies and nickels.
sites.google.com/site/figureoutfractions/fractions-in-everyday-life
Fractions are used in baking to tell how much of an ingredient to use.
Fractions are used in telling time; each minute is a fraction of the hour.
Money is another place fractions are used. For example, a quarter is one fourth of a dollar (1/4). A dime is one-tenth, represented by 1/10. We could continue by talking about pennies and nickels.
sites.google.com/site/figureoutfractions/fractions-in-everyday-life
Interactive Fraction Creator!
https://apps.mathlearningcenter.org/fractions/
Fraction Manipulatives
http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/mathematics/ebook_assets/vmf/VMF-Interface.html
https://apps.mathlearningcenter.org/fractions/
Fraction Manipulatives
http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_assets/mathematics/ebook_assets/vmf/VMF-Interface.html
Fractions Videos
Watch these various videos to help you understand fractions.
Fraction Vocabulary Study
These vocabulary activities will help you with understanding the terms and how they are connected in math.
https://cindyelkins.edublogs.org/category/fractions/
Fraction Kahoot Games
Click the button below for a Kahoot game about fractions.
Fraction Website Games
www.mathgames.com/skill/1.11-what-fraction-does-this-shape-show
www.education.com/game/geometry-picnic/
www.education.com/game/geometry-picnic/
Adding and Subtracting Fractions With Like Denominators
M.EE.7.NS.1 - Add fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) with sums less than or equal to one.
Learning Goal:
• Level 2-3 – I will add fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) to solve a math problem.
• Level 1 – I will count fractional objects.
Essential Questions:
• How can I represent these fractions?
• What is the relationship between the two fractions?
•What is the sum of two fractions?
• Which part of the fractions do I add?
Vocabulary:
• numerator - the top number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts of the whole taken.
• denominator - the bottom number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts the whole has been divided into.
• equal - alike in size, value or amount to something else.
• fraction - a representation of a division of a number; a part of a whole.
• half - either of two equal parts of something.
• quarter - one of four equal parts into which something is divided.
• whole number - a positive integer or zero. 1, 15, 30 and 894 are examples.
Learning Goal:
• Level 2-3 – I will add fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) to solve a math problem.
• Level 1 – I will count fractional objects.
Essential Questions:
• How can I represent these fractions?
• What is the relationship between the two fractions?
•What is the sum of two fractions?
• Which part of the fractions do I add?
Vocabulary:
• numerator - the top number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts of the whole taken.
• denominator - the bottom number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts the whole has been divided into.
• equal - alike in size, value or amount to something else.
• fraction - a representation of a division of a number; a part of a whole.
• half - either of two equal parts of something.
• quarter - one of four equal parts into which something is divided.
• whole number - a positive integer or zero. 1, 15, 30 and 894 are examples.
Learning Intention: Students will add and subtract fractions with common denominators.
Success Criteria: Students will be successful when they can independently add or subtract fractions with denominators of 10 and 100.
Success Criteria: Students will be successful when they can independently add or subtract fractions with denominators of 10 and 100.
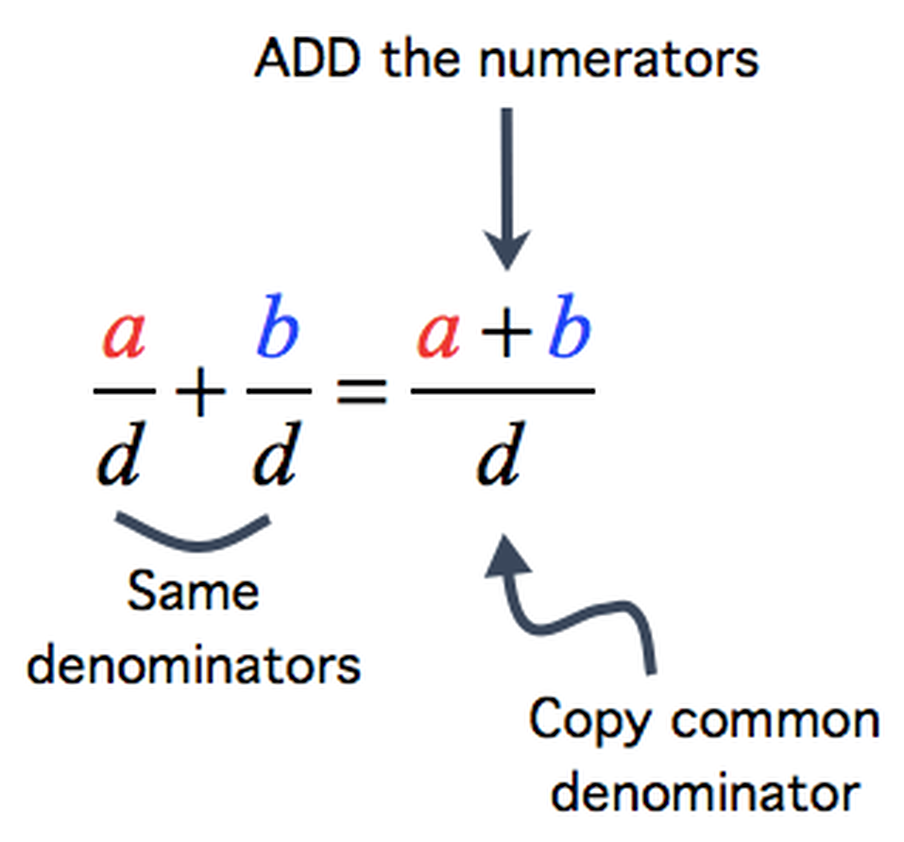
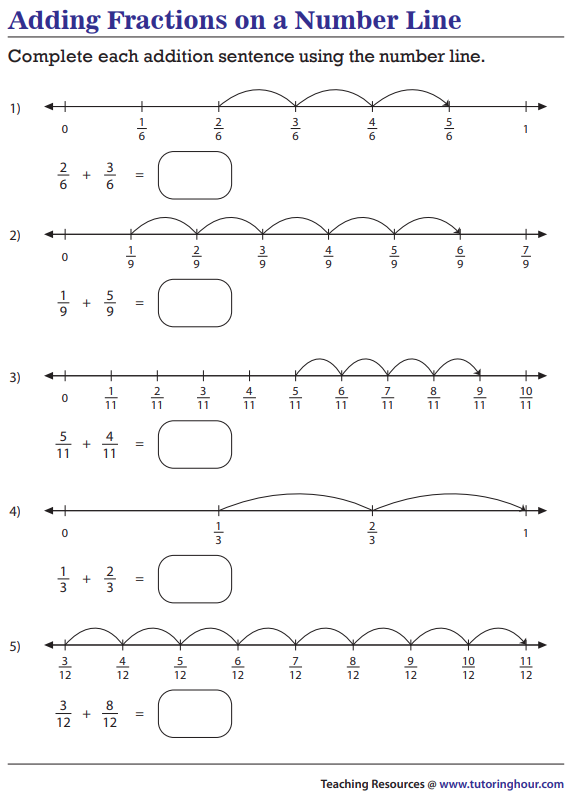
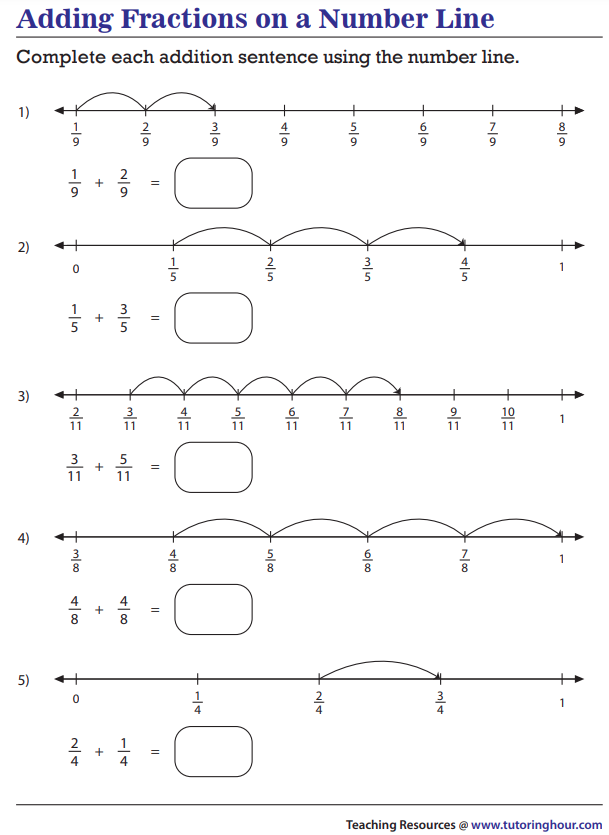
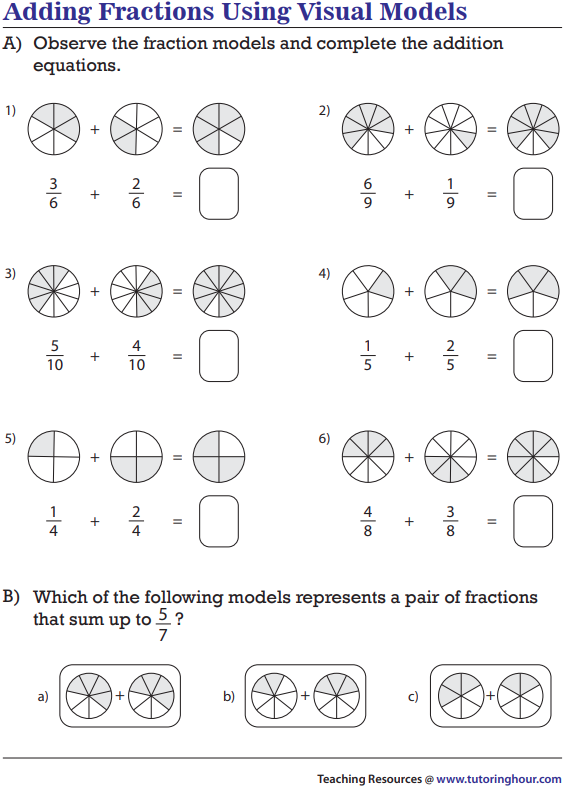
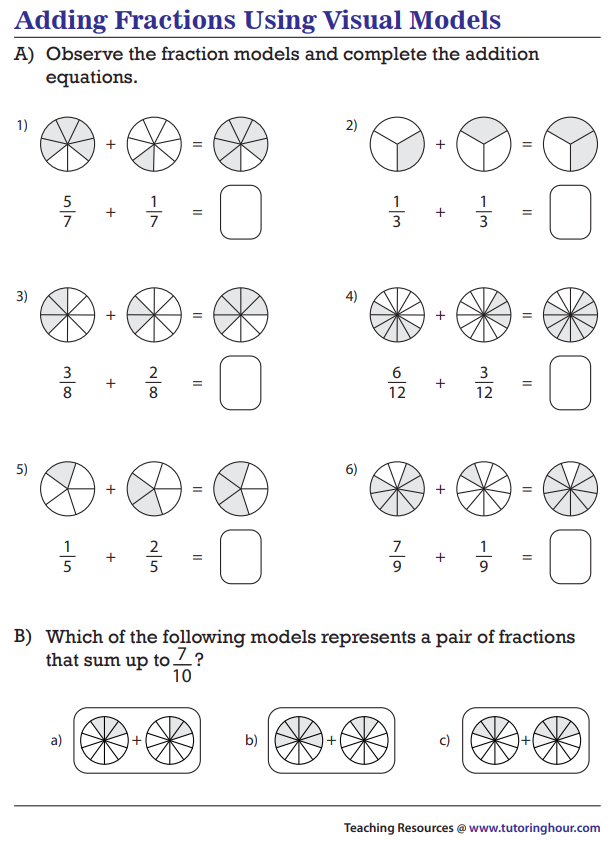
Strategy
To add fractions there are Two Simple Steps:
Step 1: Make sure the bottom numbers (the denominators) are the same.
Step 2: Add the top numbers (the numerators), put that answer over the denominator.
Step 1: Make sure the bottom numbers (the denominators) are the same.
Step 2: Add the top numbers (the numerators), put that answer over the denominator.
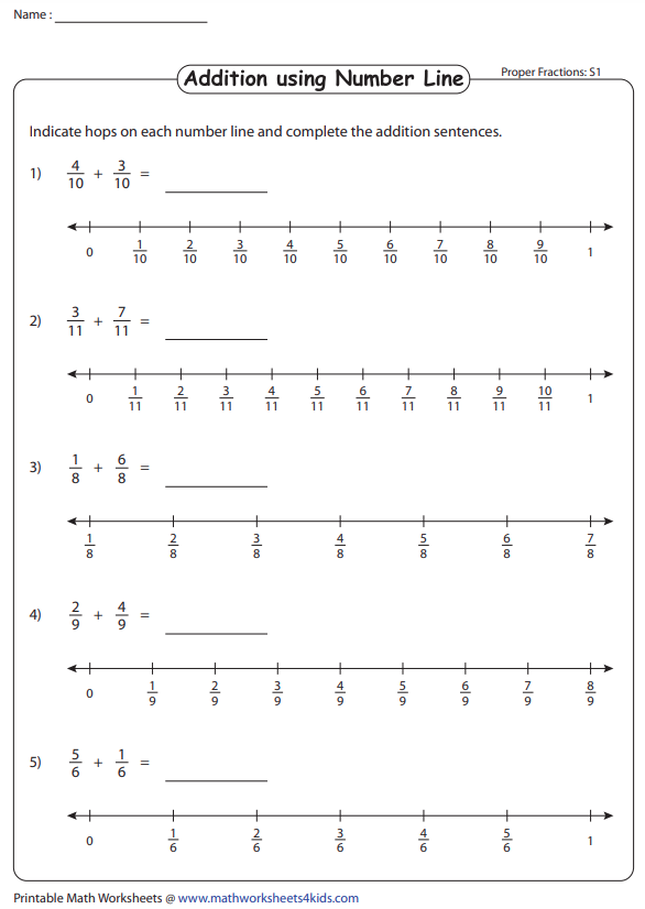
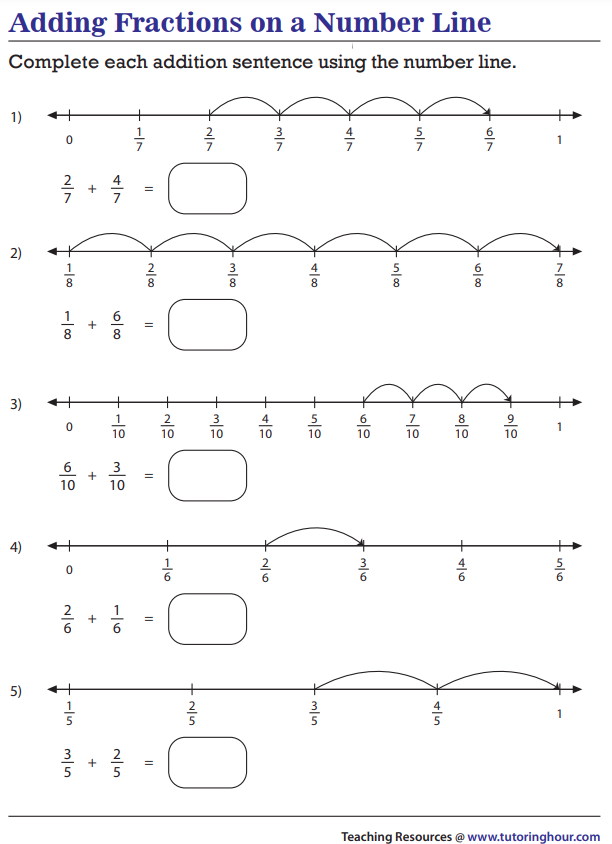
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| _usr_local_src_education.com_files_static_lesson-plans_adding-fractions-on-number-lines_adding-fractions-on-number-lines.pdf | |
| File Size: | 663 kb |
| File Type: | |
Adding Fractions With Like Denominators
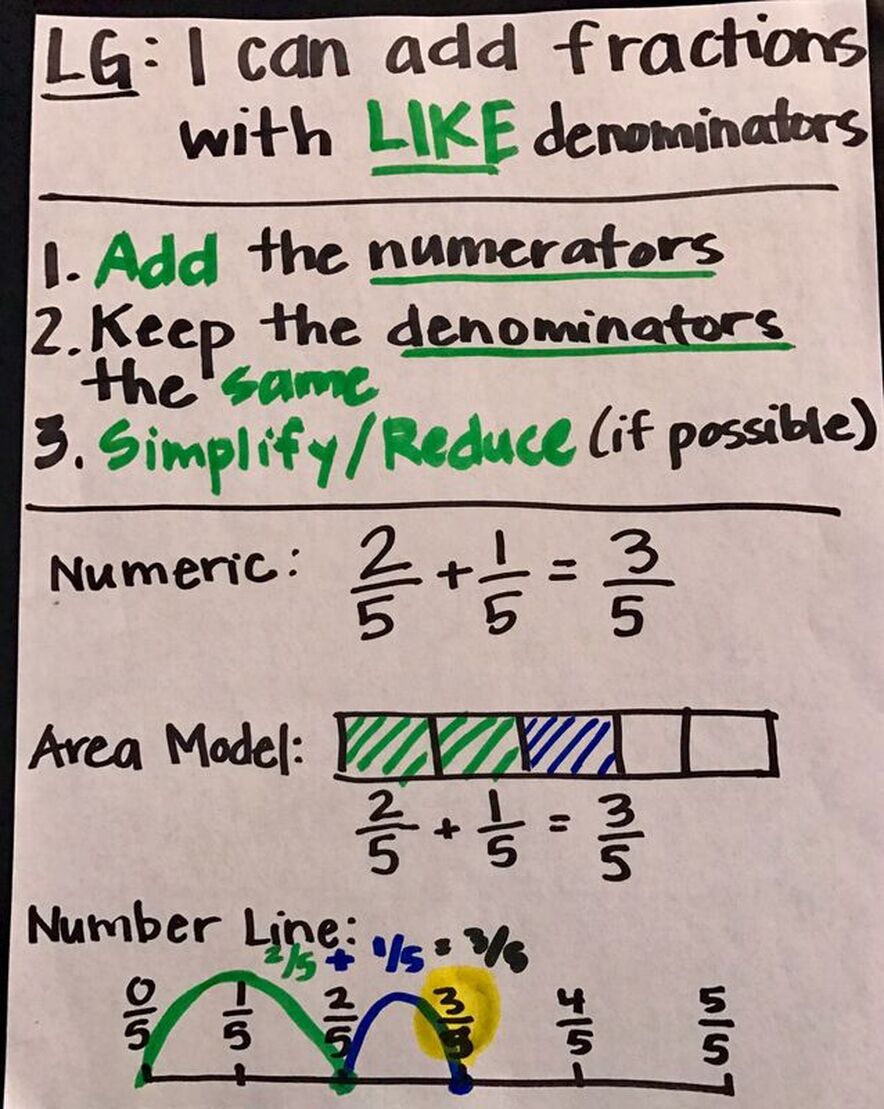
https://www.pinterest.at/pin/410601691012894605/
Adding Like Fractions, an interactive worksheet by ArmandoBorlaza
liveworksheets.com
liveworksheets.com
Adding Fractions with like denominators, an interactive worksheet by DNThompson
liveworksheets.com
liveworksheets.com
Adding Fractions With Like Denominator Games
www.sheppardsoftware.com/math/fractions/addition-game/
www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/fractions/mathman_add_subtract_fractions.htm
www.education.com/game/jungle-fractions-like-denominators/
www.sheppardsoftware.com/mathgames/fractions/mathman_add_subtract_fractions.htm
www.education.com/game/jungle-fractions-like-denominators/
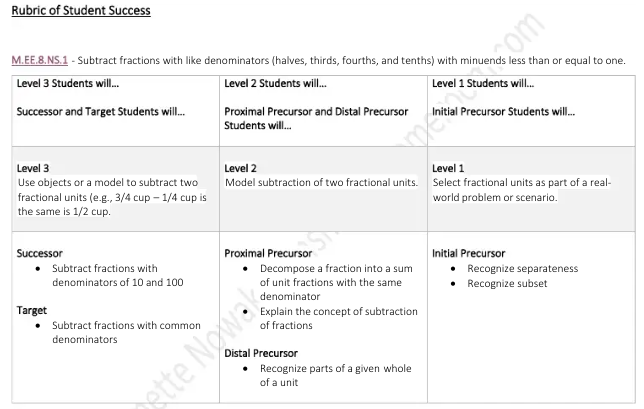
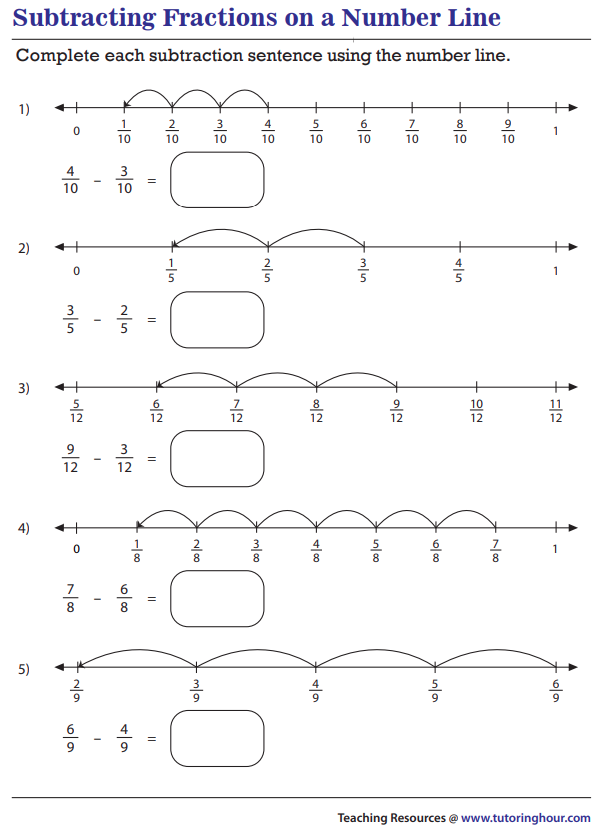
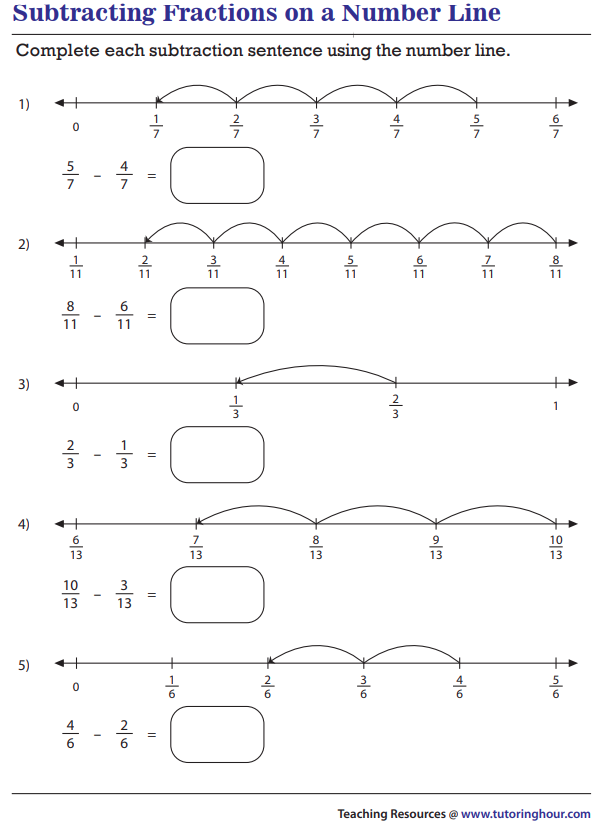
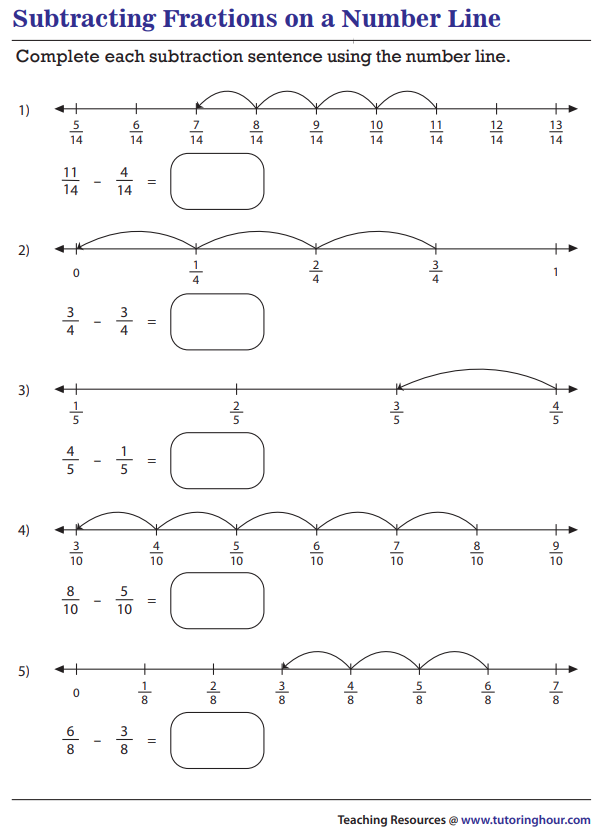
Subtracting Fractions With Like Denominator
M.EE.8.NS.1 - Subtract fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) with minuends less than or equal to one.
Learning Goal:
• Level 2-3 – I will subtract fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) to solve a math problem.
• Level 1 – I will subtract fractional objects.
Essential Questions:
• How can I represent these fractions?
• What is the relationship between the two fractions?
• What is the difference of two fractions?
• Which part of the fractions do I subtract?
• Why do I not subtract the denominators?
• How can I express a fraction as a decimal?
• Which hundredths is larger/smaller (from a real-world example)?
Vocabulary:
• numerator - the top number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts of the whole taken.
• denominator - the bottom number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts the whole has been divided into.
• equal - alike in size, value or amount to something else.
• fraction - a representation of a division of a number; a part of a whole.
• half - either of two equal parts of something.
• quarter - one of four equal parts into which something is divided.
• whole number - a positive integer or zero. 1, 15, 30 and 894 are examples.
Learning Goal:
• Level 2-3 – I will subtract fractions with like denominators (halves, thirds, fourths, and tenths) to solve a math problem.
• Level 1 – I will subtract fractional objects.
Essential Questions:
• How can I represent these fractions?
• What is the relationship between the two fractions?
• What is the difference of two fractions?
• Which part of the fractions do I subtract?
• Why do I not subtract the denominators?
• How can I express a fraction as a decimal?
• Which hundredths is larger/smaller (from a real-world example)?
Vocabulary:
• numerator - the top number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts of the whole taken.
• denominator - the bottom number in a fraction, which shows the number of parts the whole has been divided into.
• equal - alike in size, value or amount to something else.
• fraction - a representation of a division of a number; a part of a whole.
• half - either of two equal parts of something.
• quarter - one of four equal parts into which something is divided.
• whole number - a positive integer or zero. 1, 15, 30 and 894 are examples.
Learning Intention: Students will add and subtract fractions with common denominators.
Success Criteria: Students will be successful when they can independently add or subtract fractions with denominators of 10 and 100.
Success Criteria: Students will be successful when they can independently add or subtract fractions with denominators of 10 and 100.
Your browser does not support viewing this document. Click here to download the document.
| _usr_local_src_education.com_files_static_lesson-plans_el-support-lesson-modeling-fraction-subtraction_el-support-lesson-modeling-fraction-subtraction.pdf | |
| File Size: | 981 kb |
| File Type: | |
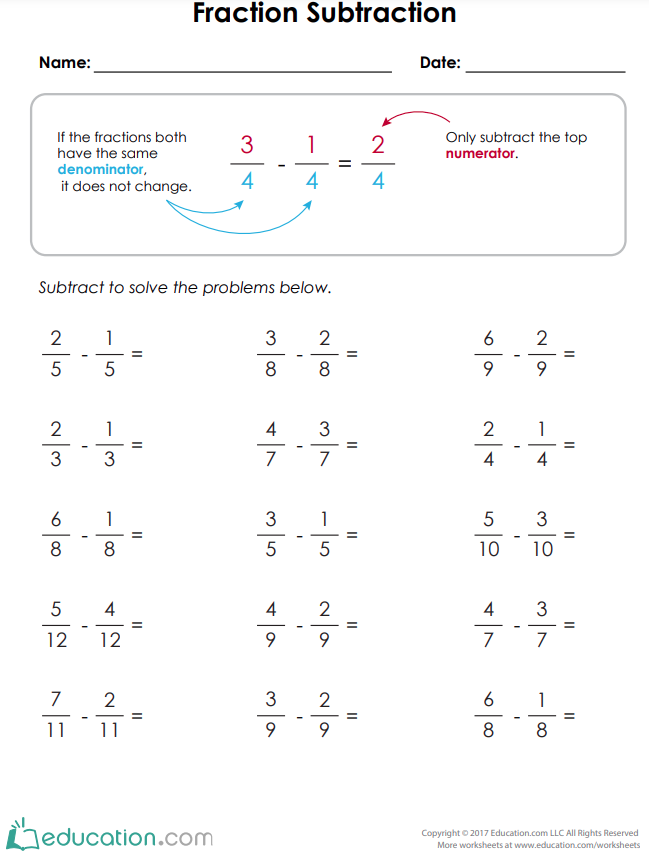
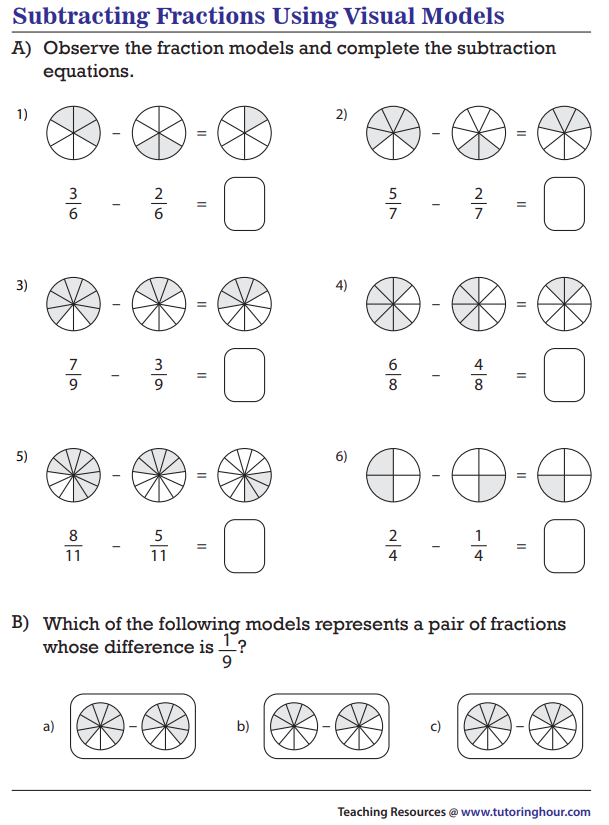
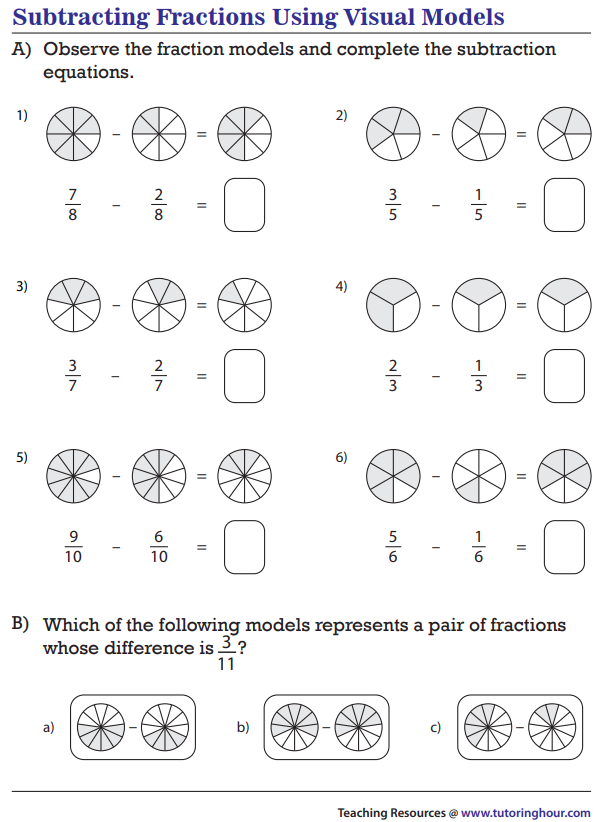
Strategy
To subtract fractions there are Two Simple Steps:
Step 1: Make sure the bottom numbers (the denominators) are the same.
Step 2: Subtract the top numbers (the numerators), put that answer over the denominator.
Step 1: Make sure the bottom numbers (the denominators) are the same.
Step 2: Subtract the top numbers (the numerators), put that answer over the denominator.